In the world of ENT (ear, nose, and throat) health, conditions like sinusitis, tonsillitis, and ear infections often dominate discussions. However, one lesser-known yet significant condition is adenoidid. This article offers a detailed and human-written explanation of adenoidid, including what it is, how it occurs, its symptoms, diagnosis methods, treatments, and prevention tips. Whether you’re a concerned parent or an adult dealing with persistent symptoms, understanding adenoidid is the first step toward better health.
What Is Adenoidid?
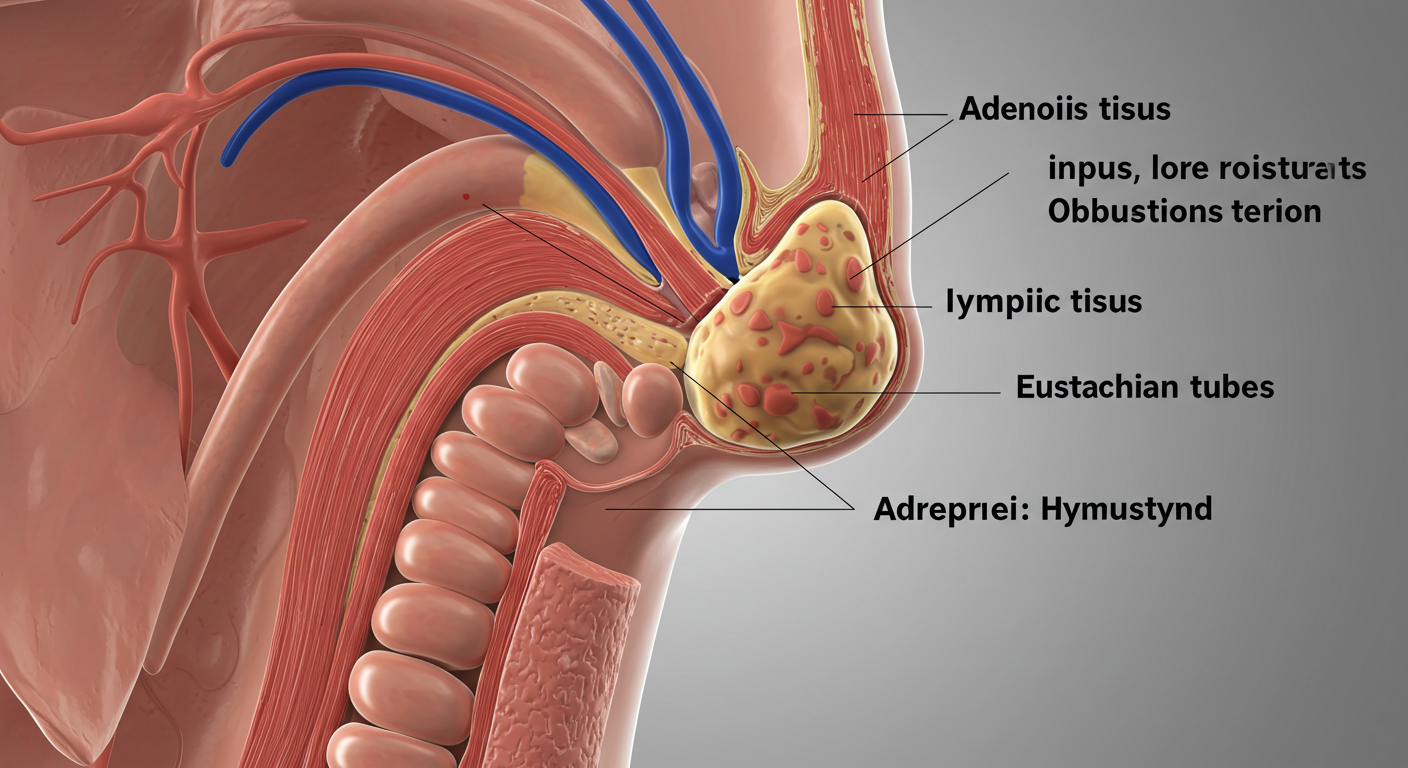
Adenoidid is a rare medical condition characterized by inflammation or infection of the adenoids. The adenoids are small masses of lymphatic tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity, above the roof of the mouth. They play a vital role in the immune system by trapping harmful bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose.
When these tissues become inflamed, either due to infection or chronic irritation, the result is a condition known as adenoidid. While often confused with adenoid hypertrophy or tonsillitis, adenoidid specifically refers to the inflammation aspect of the adenoids, not just their enlargement.
Causes of Adenoidid
Several factors may lead to adenoidid. These include:
1. Bacterial or Viral Infections
The most common cause of adenoidid is infection. Common cold viruses, influenza, or bacterial pathogens like Streptococcus pyogenes can infect the adenoids, leading to inflammation.
2. Allergic Reactions
Environmental allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander can cause persistent irritation, resulting in adenoidid in sensitive individuals.
3. Repeated Upper Respiratory Infections
Children and adults with frequent colds or sinus infections are more prone to develop adenoidid due to the continuous exposure of adenoids to infectious agents.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Adenoidid
The symptoms of adenoidid can vary based on the severity and duration of the inflammation. Here are the most common indicators:
-
Nasal Congestion: Blocked nasal passages, resulting in mouth breathing.
-
Snoring or Sleep Apnea: Enlarged or inflamed adenoids can obstruct airflow during sleep.
-
Sore Throat and Ear Pain: Due to proximity to the Eustachian tubes, adenoidid can cause ear pressure or infections.
-
Bad Breath (Halitosis): Ongoing infection or postnasal drip from inflamed adenoids can lead to foul-smelling breath.
-
Persistent Cough: Especially at night, due to drainage from inflamed adenoids.
-
Fatigue and Irritability: Caused by disrupted sleep and constant discomfort.
Diagnosing Adenoidid: What to Expect
If you or your child exhibit symptoms of adenoidid, medical diagnosis is essential. An ENT specialist typically performs the following:
1. Physical Examination
The doctor may examine the throat, nose, and ears using a small mirror or nasal endoscope.
2. Imaging Tests
X-rays or CT scans can help visualize enlarged or inflamed adenoids and rule out other conditions.
3. Lab Tests
In cases involving infection, swabs or cultures may be collected to determine the bacterial or viral cause.
Accurate diagnosis ensures the right treatment plan and prevents complications associated with untreated adenoidid.
Treatment Options for Adenoidid
Treating adenoidid depends on the cause, severity, and patient age. Common treatments include:
1. Antibiotics
If the inflammation is due to a bacterial infection, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed. It’s crucial to complete the full course to prevent recurrence.
2. Anti-inflammatory Medications
Steroid nasal sprays or oral corticosteroids can reduce swelling and ease symptoms.
3. Surgery (Adenoidectomy)
In cases of chronic adenoidid or when non-surgical treatments fail, surgical removal of the adenoids (adenoidectomy) might be recommended. It’s a simple outpatient procedure with minimal recovery time.
4. Supportive Care
Using humidifiers, saline nasal rinses, and ensuring proper hydration can also alleviate symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Adenoidid
Preventing adenoidid involves general hygiene and immune-boosting practices:
-
Wash Hands Frequently: Reduces the risk of respiratory infections.
-
Avoid Smoking or Polluted Environments: Secondhand smoke and air pollution can irritate the respiratory tract.
-
Limit Exposure to Allergens: Keep the home environment clean, especially bedrooms.
-
Boost Immunity: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep strengthen the immune system.
For children especially, maintaining good hygiene and timely vaccination schedules can reduce the incidence of adenoidid.
Adenoidid in Children vs. Adults
Children:
Adenoidid is more common in children aged 3–7. Their adenoids are more active and larger relative to their nasal cavity size, which makes inflammation more symptomatic.
Adults:
Though rare, adenoidid can also affect adults. When it does, it may be due to chronic sinus problems, allergies, or an underlying health condition. Adults with persistent nasal obstruction should consult an ENT to rule out serious conditions.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from adenoidid depends on the treatment used. If antibiotics or steroids are prescribed, symptoms usually subside within a few days. For surgical patients:
-
Post-surgery recovery usually takes 1 to 2 weeks.
-
Avoid strenuous activity during this period.
-
Follow-up checkups ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of complications.
It’s essential to follow the medical advice provided by the healthcare provider for a complete and safe recovery.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if:
-
Symptoms persist for more than 10 days.
-
You or your child experience breathing difficulties.
-
There is frequent recurrence of infections.
-
Snoring is severe or associated with pauses in breathing.
Prompt medical attention can prevent chronic issues and help manage adenoidid effectively.
Final Thoughts: Why Awareness of Adenoidid Matters
Adenoidid may not be the most commonly discussed medical condition, but its impact on breathing, sleep quality, and overall health is undeniable. Whether you’re a parent noticing unusual sleep patterns in your child or an adult facing frequent nasal blockages, knowing the signs of adenoidid can guide you toward timely diagnosis and treatment.
Maintaining good hygiene, seeking medical help when needed, and staying informed are your best tools against conditions like adenoidid. As with all health concerns, early intervention is key.